Measuring Targeting Efficiency
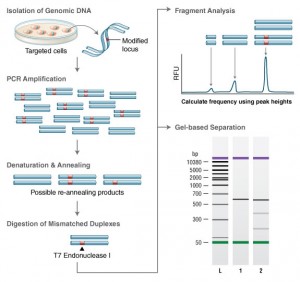
A widely used method to identify mutations is the T7 Endonuclease I mutation detection assay (1,2). This assay detects heteroduplex DNA that results from the annealing of a DNA strand, including desired mutations, with a wild-type DNA strand. The EnGen Mutation Detection Kit provides optimized reagents for performing robust T7 Endonuclease-based detection of genome editing events.
Reyon, D. et al. (2012) Nat. Biotechnol., 30(5):460-5
Vouillot, L., et al. (2015) G3 (Bethesda), 5(3):407-15
Genomic DNA is amplified with primers bracketing the modified locus. PCR products are then denatured and re-annealed yielding three classes of possible structures. Duplexes containing a mismatch greater than one base are digested by T7 Endonuclease I. The DNA is then electrophoretically separated and fragment analysis is used to estimate targeting efficiency.
Further information can be found in our Technical Resources section or at neb.com. Information on trademarks can be found here.