Golden Gate Assembly
The efficient and seamless assembly of DNA fragments, commonly referred to as Golden Gate assembly, has its origins in 1996, when for the first time it was shown that multiple inserts could be assembled into a vector backbone using only the sequential or simultaneous activities of a single type IIS restriction enzyme and T4 DNA ligase.
- The overhang sequence created is not dictated by the REase, and therefore no scar sequence is introduced.
- The fragment-specific sequence of the overhangs allows orderly assembly of multiple fragments simultaneously.
- The restriction site is eliminated from the ligated product, so digestion and ligation can be carried out simultaneously.
Golden Gate Assembly and its derivative methods exploit the ability of Type IIS restriction endonucleases (REases) to cleave DNA outside of the recognition sequence. The inserts and cloning vectors are designed to place the Type IIS recognition site distal to the cleavage site, such that the Type IIS REase can remove the recognition sequence from the assembly.
The net result is the ordered and seamless assembly of DNA fragments in one reaction. The accuracy of the assembly is dependent on the length of the overhang sequences. Therefore, Type IIS REases that create 4-base overhangs (such as BsaI/BsaI-HFv2, BbsI/BbsI-HF, BsmBI und Esp3I. are preferred.
Insert assembly calls for careful design of overhangs to direct the assembly, as well as verification that the Type IIS REase sites used are not present in the fragments for the assembly of the expected product. The use of web tools such as the NEBridge Golden Gate Tool greatly simplifies both processes, making Golden Gate Assembly a robust technology that assembles multiple DNA fragments, even if repetitive elements are present and can, if wished, introduce multiple site-directed mutations. Golden Gate Assembly has been widely used in the construction of custom-specific TALENs for in vivo gene editing, among other applications.
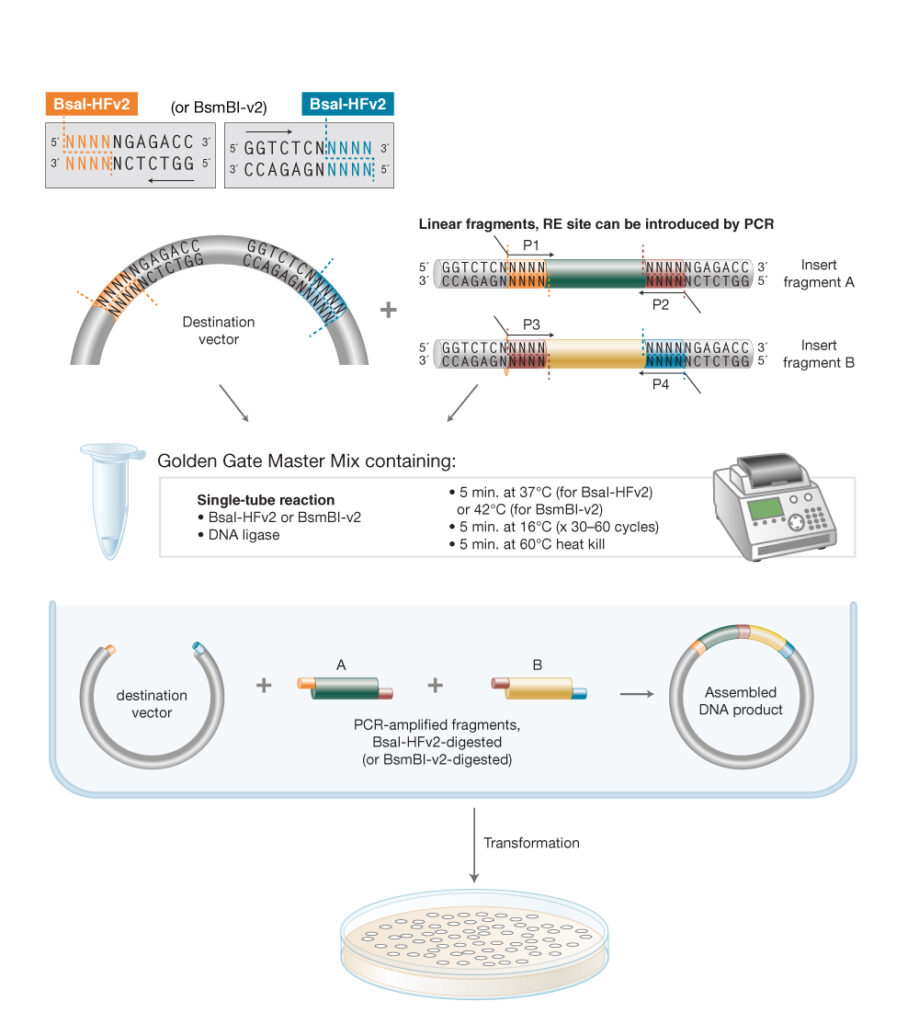
Golden Gate Workflow
Golden Gate assembly utilizes a Type IIS restriction enzyme (REase), which cleaves outside of its non-palindromic recognition sequence and T4 DNA Ligase in a simultaneous, single-tube reaction. Inserts and vectors are designed to place the Type IIS recognition site distal to the cleavage site. Cut sites can be introduced by PCR primers, if needed. During the reaction, the Type IIS REase removes the recognition sequence from the assembly with each fragment bearing the designed 3- or 4-base complementary overhangs that direct the assembly. The fragments anneal, T4 DNA Ligase seals the nicks, and the final construct accumulates over time. Cycling between optimal restriction and ligation temperature further enhances the Golden Gate efficiency. Golden Gate Assembly can be used for ordered assembly of 2–50+ fragments simultaneously.
Product Table
As of: 01.01.2024
Further information can be found in our Technical Resources section or at neb.com. Information on trademarks can be found here.