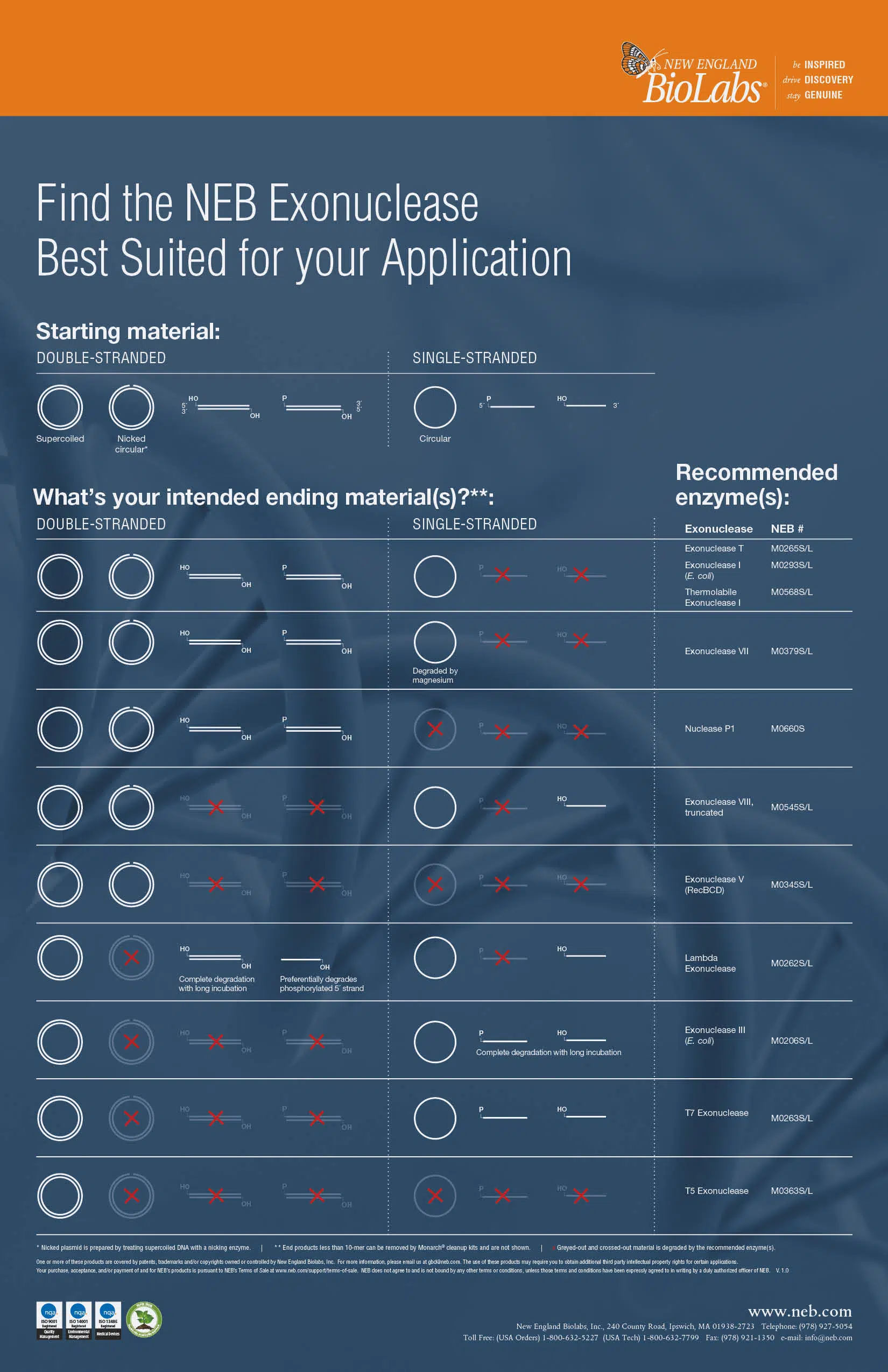
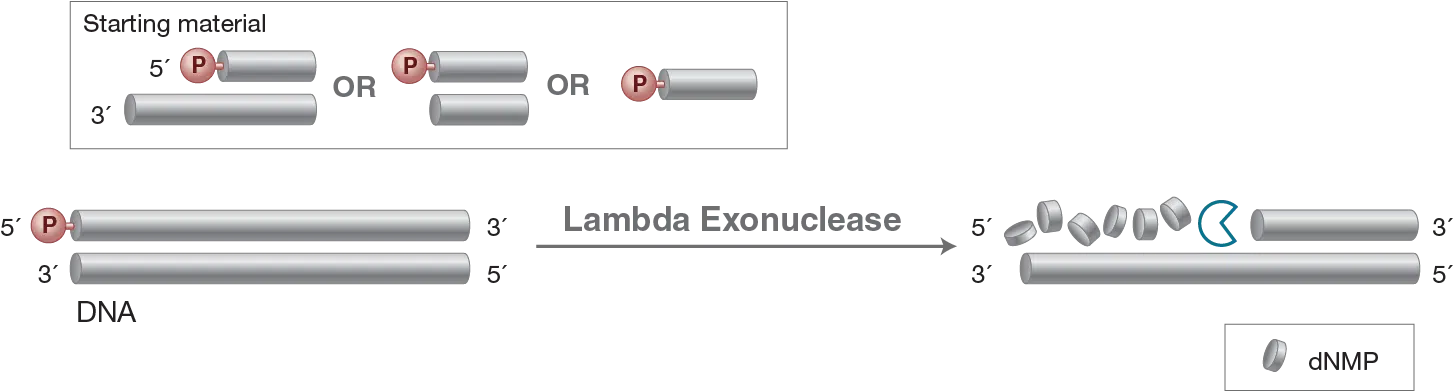Exonucleases and endonucleases are used in many of today’s molecular biology workflows and applications.
Did you know that NEB offers the largest supply of these important tools, and has a team of experts studying the function and optimization of these enzymes?
We also offer several helpful tools to help you find the best enzyme to facilitate your work.
Key Examples:
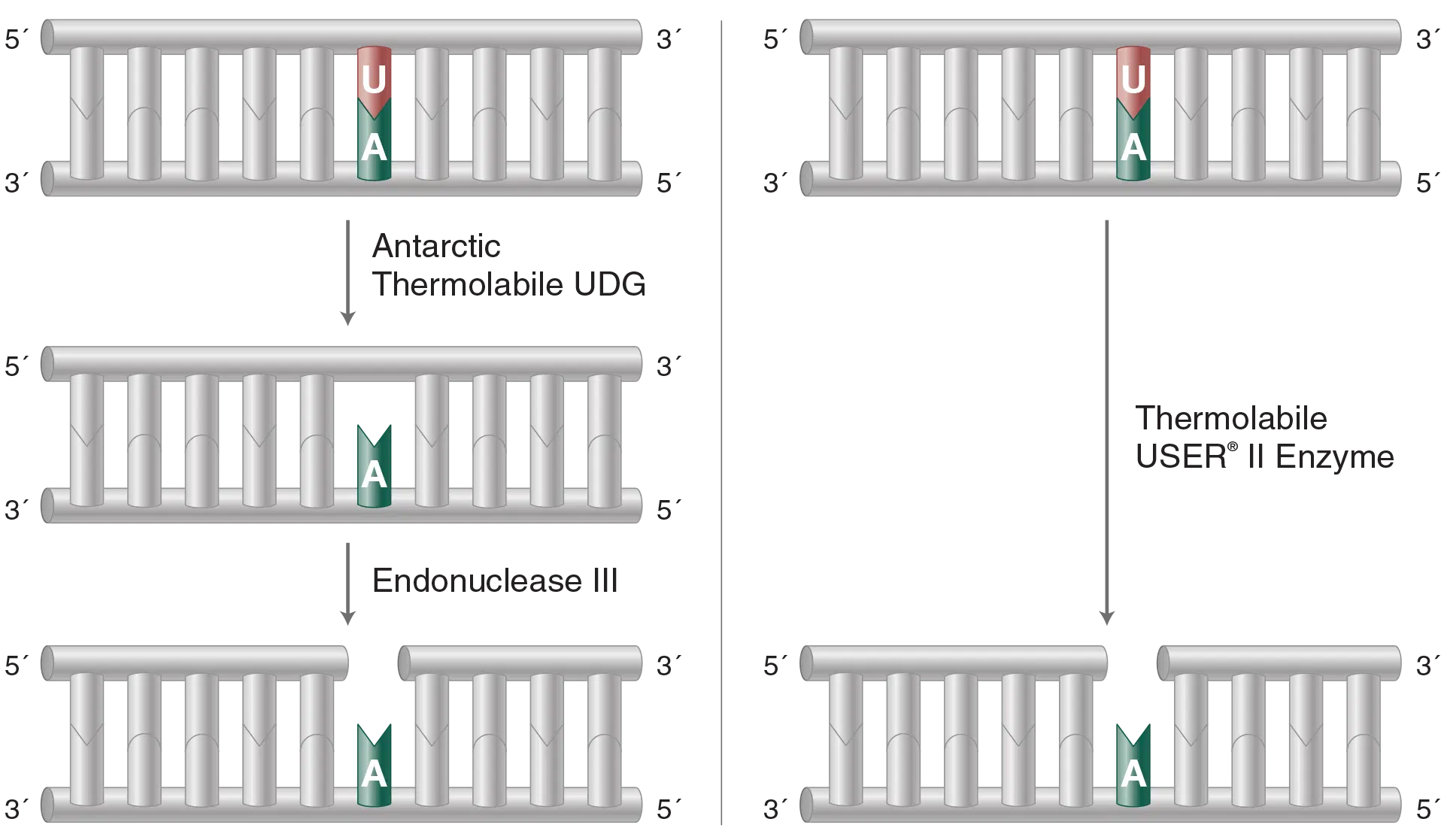
Thermolabile USER II Enzyme
Thermolabile USER (Uracil-Specific Excision Reagent) II Enzyme generates a single nucleotide gap at the location of a uracil residue. It can be 100% inactivated at temperatures >65°C, streamlining workflows and enabling DNA to be used directly in downstream applications.
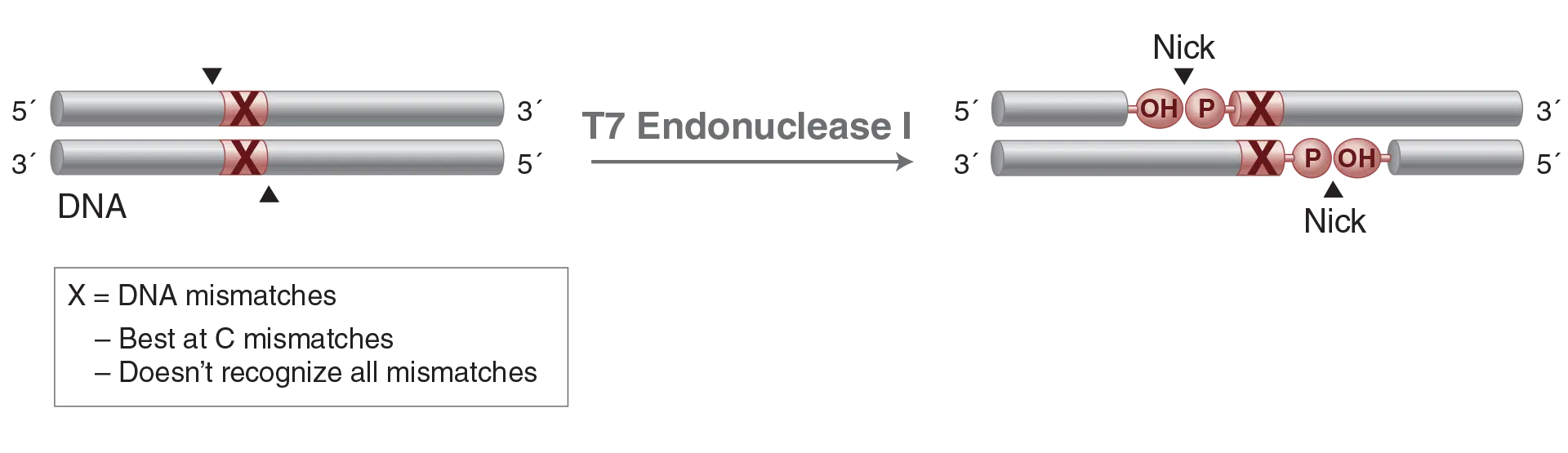
T7 Endonuclease I
T7 Endonuclease I recognizes and cleaves non-perfectly matched DNA, cruciform DNA structures,
Holliday structures or junctions, heteroduplex DNA and more slowly, nicked double-stranded DNA. The cleavage site is at the first, second or third phosphodiester bond that is 5´ to the mismatch. The protein is the product of T7 gene 3.
Thermostable FEN1
Thermostable Flap Endonuclease 1, FEN1, catalyzes the cleavage of 5´ DNA flaps from branched double stranded DNA substrates, creating a 5´ phosphate terminus. FEN1 products can be ligated by DNA ligase to create double-stranded DNA. In vivo, FEN1 is an essential component of the Okazaki fragment maturation pathway, and also plays a role in base excision repair.
Lambda Exonuklease
Lambda Exonuclease catalyzes the removal of nucleotides from linear or nicked double-stranded DNA in the 5´ to 3´ direction. This enzyme is highly processive. The preferred substrate is 5´-phosphorylated double-stranded DNA, although non-phosphorylated substrates are degraded at a greatly reduced rate.
Thermolabile Exonuclease I
Thermolabile Exonuclease I catalyzes the removal of nucleotides from linear single-stranded DNA in
the 3´ to 5´ direction. Unlike Exonuclease I (NEB #M0293), Thermolabile Exonuclease I can be heat
inactivated at 80°C in one minute.
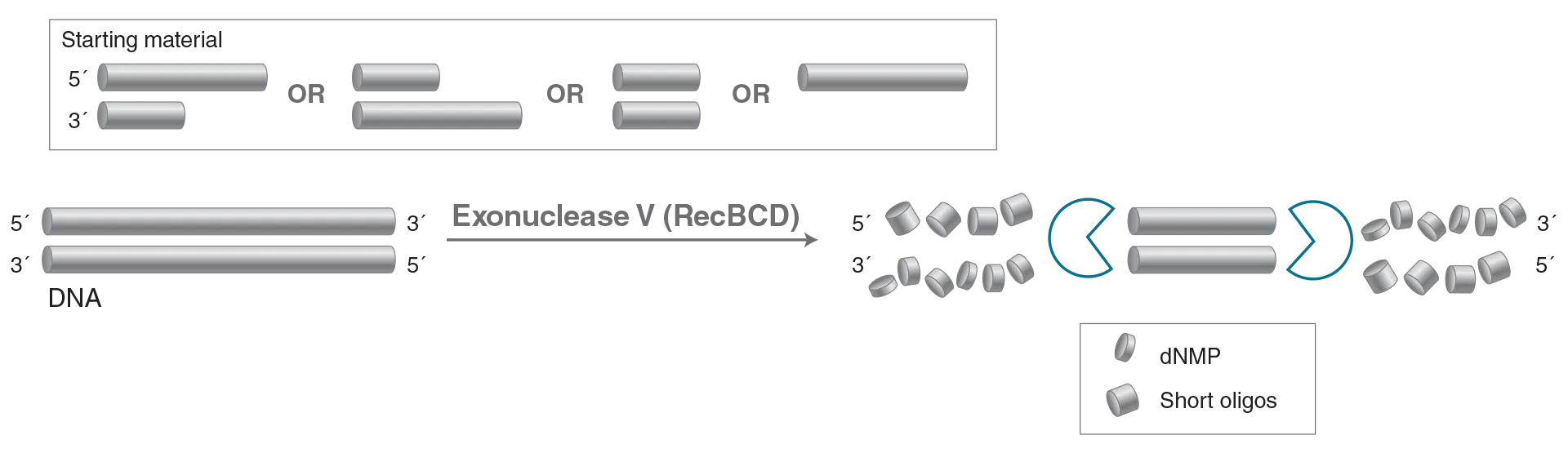
Exonuclease V (RecBCD)
Exonuclease V (RecBCD) is a DNA specific exonuclease that also acts as an endonuclease on singlestranded DNA. It initiates at both 5′ and 3′ termini of linear double-stranded DNA and cleaves linear
double-stranded DNA in both the 3′ to 5′ and 5′ to 3′ directions. It requires ATP in the reaction.
Interested in learning more?
Access our extensive selection of tools and resources using the links below.
How well do you know your Exo- and Endonucleases?
Get a free Exonuclease poster and Endonuclease card:
Further information can be found in our Technical Resources section or at neb.com. Information on trademarks can be found here.